Contents
olymplike.m
From A First Course in Machine Learning, Chapter 2. Simon Rogers, 01/11/11 [simon.rogers@glasgow.ac.uk] Likelihood increases as model complexity increases - example
clear all;close all;
Load the Olympic data
load ../data/olympics x = male100(:,1); t = male100(:,2); % Rescale x for numerical stability x = x - x(1); x = x./4;
Fit different order models with maximum likelihood
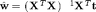
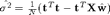
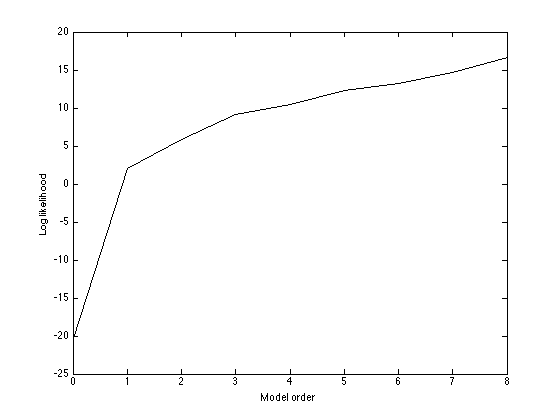
orders = [0:8]; X = []; N = length(x); for i = 1:length(orders) X = [X x.^orders(i)]; w = inv(X'*X)*X'*t; ss = (1/N)*(t'*t - t'*X*w); log_like(i) = sum(log(normpdf(t,X*w,sqrt(ss)))); end
Warning: Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND = 8.285777e-19.
Warning: Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND = 5.892273e-22.
Warning: Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND = 4.085559e-25.
Plot the model order versus the (log) likelihood
figure(1); hold off plot(orders, log_like,'k'); xlabel('Model order'); ylabel('Log likelihood');