Contents
svmhard.m
From A First Course in Machine Learning, Chapter 4. Simon Rogers, 01/11/11 [simon.rogers@glasgow.ac.uk] Hard margin SVM
clear all;close all;
Generate the data
x = [randn(20,2);randn(20,2)+4]; t = [repmat(-1,20,1);repmat(1,20,1)];
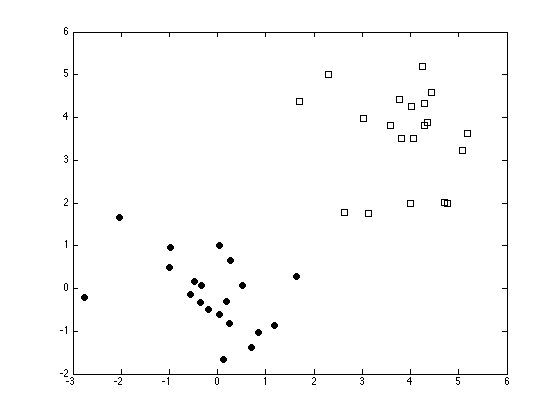
Plot the data
ma = {'ko','ks'};
fc = {[0 0 0],[1 1 1]};
tv = unique(t);
figure(1); hold off
for i = 1:length(tv)
pos = find(t==tv(i));
plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),ma{i},'markerfacecolor',fc{i});
hold on
end
Setup the optimisation problem
N = size(x,1); K = x*x'; H = (t*t').*K + 1e-5*eye(N); f = repmat(1,N,1); A = [];b = []; LB = repmat(0,N,1); UB = repmat(inf,N,1); Aeq = t';beq = 0; % Following line runs the SVM alpha = quadprog(H,-f,A,b,Aeq,beq,LB,UB); % Compute the bias fout = sum(repmat(alpha.*t,1,N).*K,1)'; pos = find(alpha>1e-6); b = mean(t(pos)-fout(pos));
Warning: Trust-region-reflective algorithm does not solve this type of problem, using active-set algorithm. You could also try the interior-point-convex algorithm: set the Algorithm option to interior-point-convex and rerun. For more help, see Choosing the Algorithm in the documentation. Optimization terminated.
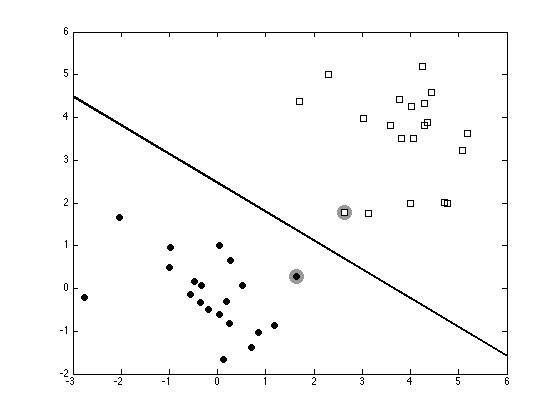
Plot the data, decision boundary and Support vectors
figure(1);hold off pos = find(alpha>1e-6); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',15,'markerfacecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6],... 'markeredgecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]); hold on for i = 1:length(tv) pos = find(t==tv(i)); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),ma{i},'markerfacecolor',fc{i}); end xp = xlim; % Because this is a linear SVM, we can compute w and plot the decision % boundary exactly. w = sum(repmat(alpha.*t,1,2).*x,1)'; yp = -(b + w(1)*xp)/w(2); plot(xp,yp,'k','linewidth',2)