Contents
lapexample.m
From A First Course in Machine Learning, Chapter 4. Simon Rogers, 01/11/11 [simon.rogers@glasgow.ac.uk] The Laplace approximation to a gamma density
clear all;close all;
Define the gamma parameters
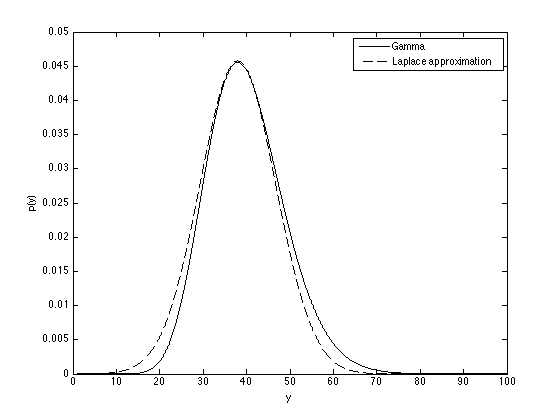
alpha = 20; beta = 0.5; % Find the mode y_hat = (alpha-1)/beta; % Find the variance ss = (alpha-1)/beta^2;
Plot the gamma and the approximate Gaussian
y = [0:0.01:100]; figure(1);hold off plot(y,gampdf(y,alpha,1/beta),'k'); %Note: Matlab uses an alternative parameterisation of the gamma function, hence the 1/beta. hold on plot(y,normpdf(y,y_hat,sqrt(ss)),'k--'); xlabel('y'); ylabel('p(y)'); legend('Gamma','Laplace approximation');
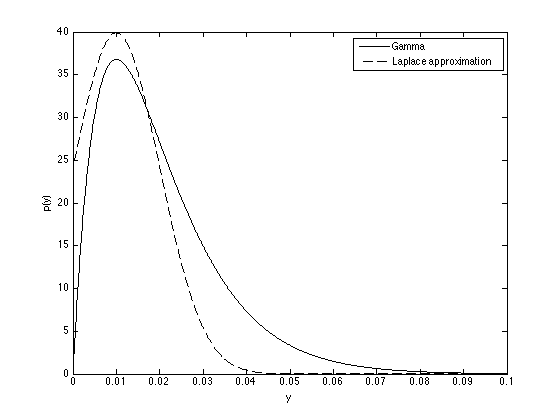
Second example
alpha = 2; beta = 100; % Find the mode y_hat = (alpha-1)/beta; % Find the variance ss = (alpha-1)/beta^2; y = [0:0.0001:0.1]; figure(1);hold off plot(y,gampdf(y,alpha,1/beta),'k'); %Note: Matlab uses an alternative parameterisation of the gamma function, hence the 1/beta. hold on plot(y,normpdf(y,y_hat,sqrt(ss)),'k--'); xlabel('y'); ylabel('p(y)'); legend('Gamma','Laplace approximation');