Contents
gmix.m
From A First Course in Machine Learning, Chapter 6. Simon Rogers, 01/11/11 [simon.rogers@glasgow.ac.uk] Fitting a Gaussian mixture
clear all;close all; path(path,'../utilities');
Load the data
load ../data/kmeansdata
Plot the data
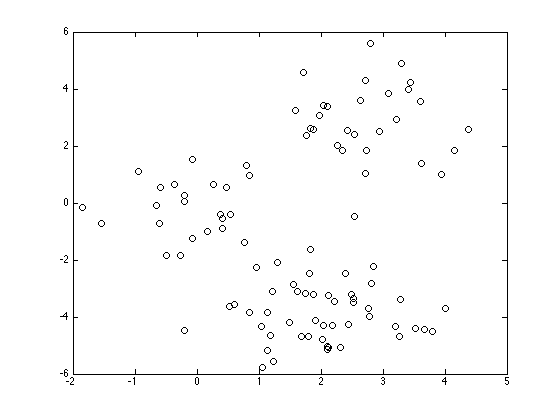
figure(1);hold off plot(X(:,1),X(:,2),'ko');
Initilaise the mixture
K = 3; % Try changing this means = randn(K,2); for k = 1:K covs(:,:,k) = rand*eye(2); end priors = repmat(1/K,1,K);
Run the algorithm
MaxIts = 100;
N = size(X,1);
q = zeros(N,K);
D = size(X,2);
cols = {'r','g','b'};
plotpoints = [1:1:10,12:2:30 40 50];
B(1) = -inf;
converged = 0;
it = 0;
tol = 1e-2;
while 1
it = it + 1;
% Update q
for k = 1:K
const = -(D/2)*log(2*pi) - 0.5*log(det(covs(:,:,k)));
Xm = X - repmat(means(k,:),N,1);
temp(:,k) = const - 0.5 * diag(Xm*inv(covs(:,:,k))*Xm');
end
% Compute the Bound on the likelihood
if it>1
B(it) = sum(sum(q.*log(repmat(priors,N,1)))) + ...
sum(sum(q.*temp)) - ...
sum(sum(q.*log(q)));
if abs(B(it)-B(it-1))<tol
converged = 1;
end
end
if converged == 1 || it>MaxIts
break
end
temp = temp + repmat(priors,N,1);
q = exp(temp - repmat(max(temp,[],2),1,K));
% Minor hack for numerical issues - stops the code crashing when
% clusters are empty
q(q<1e-60) = 1e-60;
q(q>1-1e-60) = 1e-60;
q = q./repmat(sum(q,2),1,K);
% Update priors
priors = mean(q,1);
% Update means
for k = 1:K
means(k,:) = sum(X.*repmat(q(:,k),1,D),1)./sum(q(:,k));
end
% update covariances
for k = 1:K
Xm = X - repmat(means(k,:),N,1);
covs(:,:,k) = (Xm.*repmat(q(:,k),1,D))'*Xm;
covs(:,:,k) = covs(:,:,k)./sum(q(:,k));
end
Plot the current status
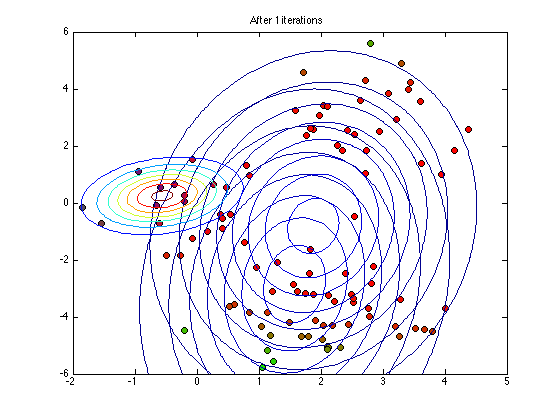
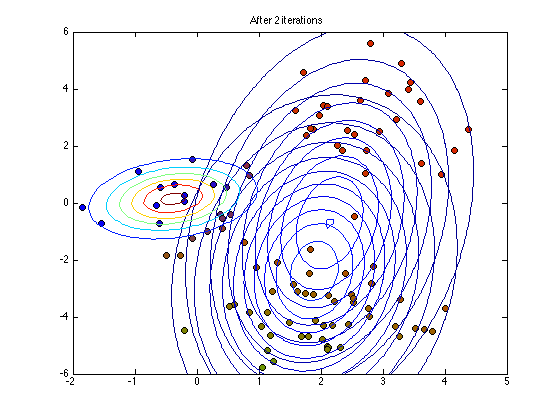
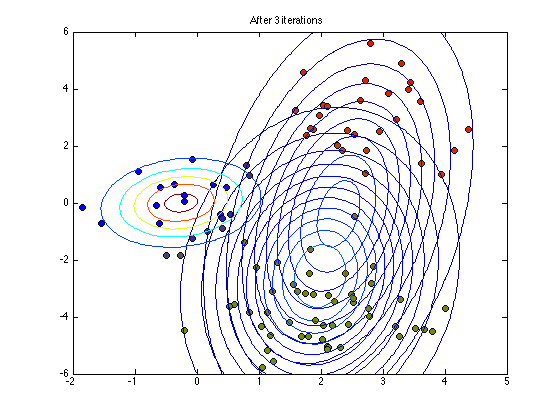
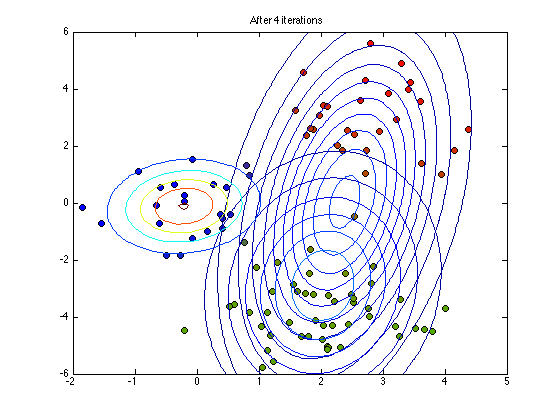
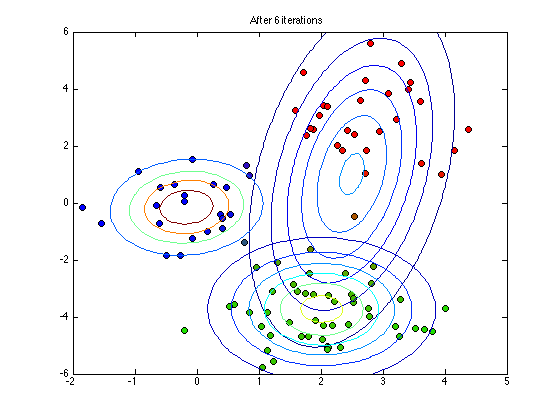
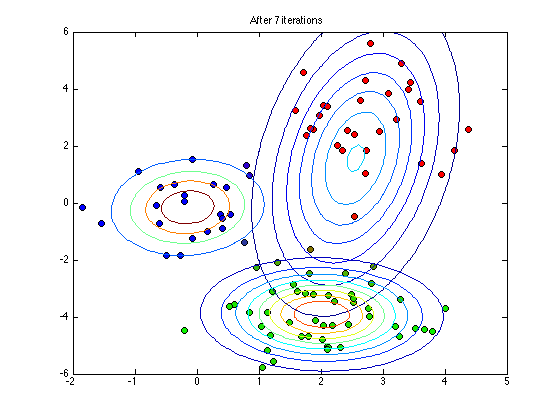
if any(it==plotpoints) figure(1);hold off % Note the following plots points using q as their RGB colour value for n = 1:N plot(X(n,1),X(n,2),'ko','markerfacecolor',q(n,:)); hold on end for k = 1:K plot_2D_gauss(means(k,:),covs(:,:,k),... -2:0.1:6,-6:0.1:6); end ti = sprintf('After %g iterations',it); title(ti) end






end
Plot the bound
figure(1);hold off plot(2:length(B),B(2:end),'k'); xlabel('Iterations'); ylabel('Bound');
