Contents
- class2d.m
- Generate the dataset
- Set the GP hyperparameters and compute the covariance function
- Newton-raphson procedure to optimise the latent function values
- Plot the optimised latent function values
- Visualise the predictive function via a large grid of test points
- Using the full GP distribution - propagating the uncertainity through the sigmoid
class2d.m
Performs binary GP classification with two-dimensional data
From A First Course in Machine Learning Simon Rogers, August 2016 [simon.rogers@glasgow.ac.uk]
clear all; close all;
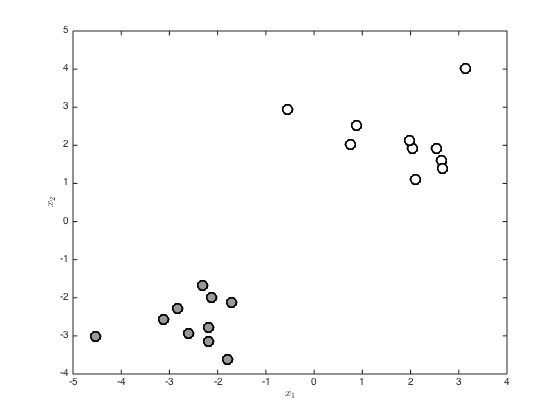
Generate the dataset
create some random data and then change the means of the two classes to seeparate them
rng(2) x = randn(20,2); x(1:10,:) = x(1:10,:) - 2; x(11:end,:) = x(11:end,:) + 2; t = [repmat(0,10,1);repmat(1,10,1)]; % Plot the data figure(); hold off pos = find(t==0); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]) hold on pos = find(t==1); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[1 1 1]) xlabel('$x_1$','interpreter','latex') ylabel('$x_2$','interpreter','latex')
Set the GP hyperparameters and compute the covariance function
alpha = 10; gamma = 0.1; N = size(x,1); C = zeros(N); for n = 1:N for m = 1:N C(n,m) = alpha*exp(-gamma*sum((x(n,:)-x(m,:)).^2)); end end
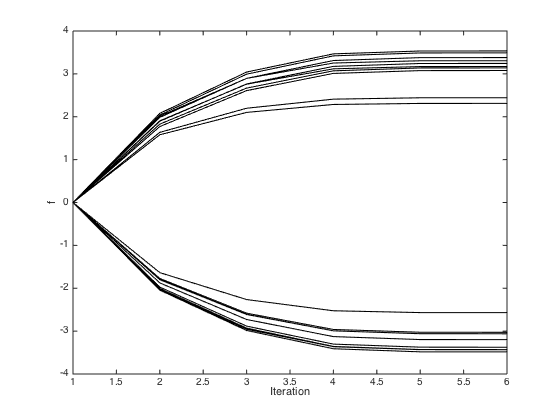
Newton-raphson procedure to optimise the latent function values
Initialise all to zero
f = repmat(0,N,1); allf = [f']; % Pre-compute the inverse of C invC = inv(C); for iteration = 2:6 g = 1./(1+exp(-f)); gra = t - g - invC*f; H = -diag(g.*(1-g)) - invC; f = f - inv(H)*gra; allf(iteration,:) = f'; end H = -diag(g.*(1-g)) - invC; % Plot the evolution of the f values figure() plot(allf,'k') xlabel('Iteration') ylabel('f')
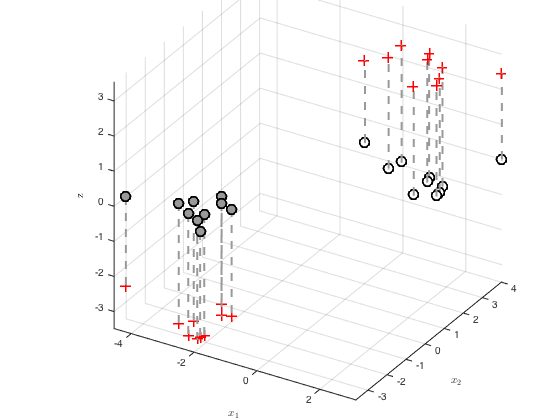
Plot the optimised latent function values
Creates a 3D plot with the function value as the z axis
figure() hold off pos = find(t==0); z = zeros(length(pos),1); plot3(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),z,'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]) hold on pos = find(t==1); z = zeros(length(pos),1); plot3(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),z,'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[1 1 1]) for n = 1:N plot3(x(n,1),x(n,2),f(n),'r+','markersize',10,'linewidth',2) plot3([x(n,1) x(n,1)],[x(n,2),x(n,2)],[0 f(n)],'k--','color',[0.6 0.6 0.6],'linewidth',2) end grid on zlabel('$f$','interpreter','latex','fontsize',20) set(gca,'cameraviewangle',8,'cameraposition',[29.3256 -49.3194 29.7317]) set(gca,'position',[0.200 0.16 0.70 0.8150]) axis tight xlabel('$x_1$','interpreter','latex') ylabel('$x_2$','interpreter','latex') zlabel('z')
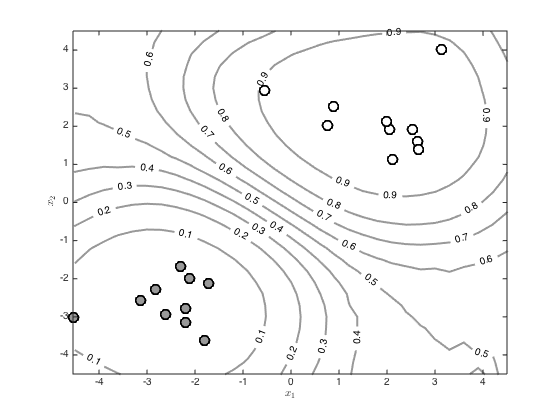
Visualise the predictive function via a large grid of test points
Create the grid
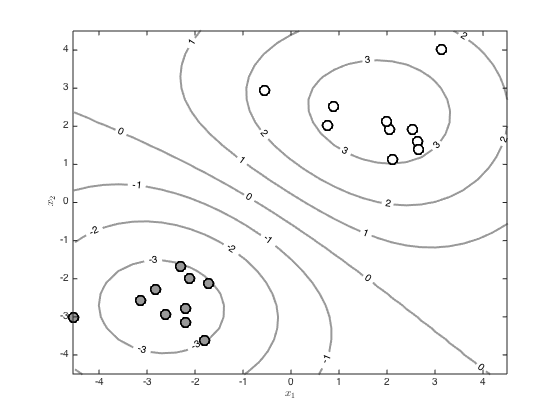
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-4.5:0.3:4.5,-4.5:0.3:4.5); testN = prod(size(X)); testX = [reshape(X,testN,1) reshape(Y,testN,1)]; % Create the test covariance function R = zeros(N,testN); for n = 1:N for m = 1:testN R(n,m) = alpha*exp(-gamma*sum((x(n,:) - testX(m,:)).^2)); end end % Compute the mean predictive latent function testf = R'*invC*f; Z = reshape(testf,size(X)); % Contour the predictions (function values, not probabilities) figure() hold off [c,h]=contour(X,Y,Z,'color',[0.6 0.6 0.6]); tl = clabel(c,h); set(h,'linewidth',2) hold on pos = find(t==0); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]) pos = find(t==1); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[1 1 1]) xlabel('$x_1$','interpreter','latex') ylabel('$x_2$','interpreter','latex') % Contour the probabilities figure() hold off [c,h]=contour(X,Y,1./(1+exp(-Z)),'color',[0.6 0.6 0.6]); tl = clabel(c,h); set(h,'linewidth',2) hold on pos = find(t==0); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]) pos = find(t==1); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[1 1 1]) xlabel('$x_1$','interpreter','latex') ylabel('$x_2$','interpreter','latex')
Warning: Text handle output is not supported for managed labels. Warning: Text handle output is not supported for managed labels.
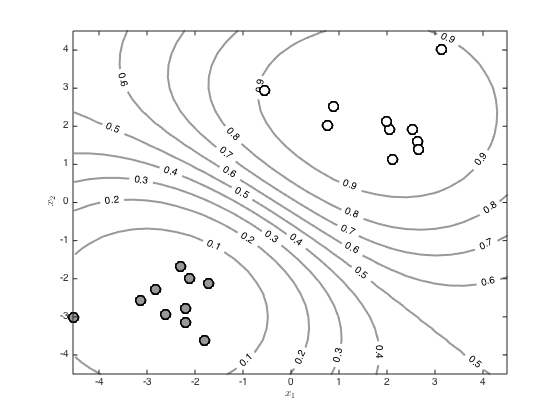
Using the full GP distribution - propagating the uncertainity through the sigmoid
pred_var = zeros(testN,1); pavg = zeros(size(testf)); minpred_var = 1e-3; % loop over the test points, computing the marginal predictive variance and % sampling function values before passing them through the sigmoid and % averaging to get a probability for n = 1:testN pred_var(n) = max(minpred_var,alpha - R(:,n)'*invC*R(:,n)); u = randn(10000,1).*sqrt(pred_var(n)) + testf(n); pavg(n) = mean(1./(1+exp(-u))); end % Contour the resulting probabilities Z = reshape(pavg,size(X)); figure() hold off [c,h]=contour(X,Y,Z,'color',[0.6 0.6 0.6]); tl = clabel(c,h); set(h,'linewidth',2) hold on pos = find(t==0); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]) pos = find(t==1); plot(x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'ko','markersize',10,'linewidth',2,'markerfacecolor',[1 1 1]) xlabel('$x_1$','interpreter','latex') ylabel('$x_2$','interpreter','latex')
Warning: Text handle output is not supported for managed labels.